Section: New Results
RapidRMSD library
Participants : Emilie Neveu, Petr Popov, Sergei Grudinin.
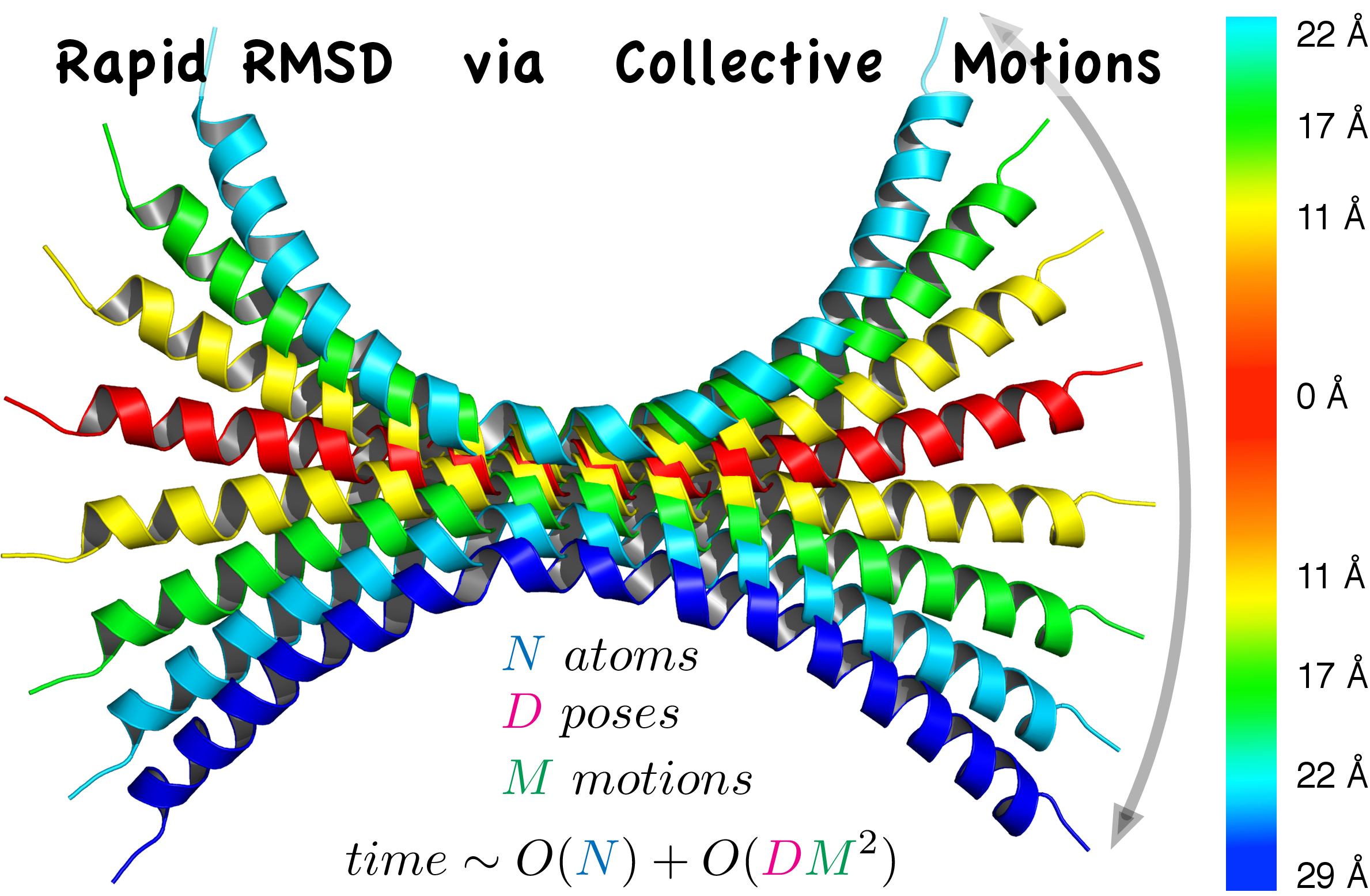
The root mean square deviation (RMSD) is one of the most used similarity criteria in structural biology and bioinformatics. Standard computation of the RMSD has a linear complexity with respect to the number of atoms in a molecule, making RMSD calculations time-consuming for the large-scale modeling applications, such as assessment of molecular docking predictions or clustering of spatially proximate molecular conformations. Previously we introduced the RigidRMSD algorithm to compute the RMSD corresponding to the rigid-body motion of a molecule [62]. Recently, we went beyond the limits of the rigid-body approximation by taking into account conformational flexibility of the molecule. We model the flexibility with a reduced set of collective motions computed with e.g. normal modes or principal component analysis.
The initialization of our algorithm is linear in the number of atoms and all the subsequent evaluations of RMSD values between flexible molecular conformations depend only on the number of collective motions that are selected to model the flexibility. Therefore, our algorithm is much faster compared to the standard RMSD computation for large-scale modeling applications. The method can be applied e.g. to cluster flexible docking or to generate pseudo-random constant-RMSD structural molecular ensembles.
The algorithm is written in C++ as the open-source RapidRMSD library governed by the BSD-compatible license, which is available at http://team.inria.fr/nano-d/software/RapidRMSD/. The constant-RMSD structural ensemble application is available at http://team.inria.fr/nano-d/software/nolb-normal-modes/.